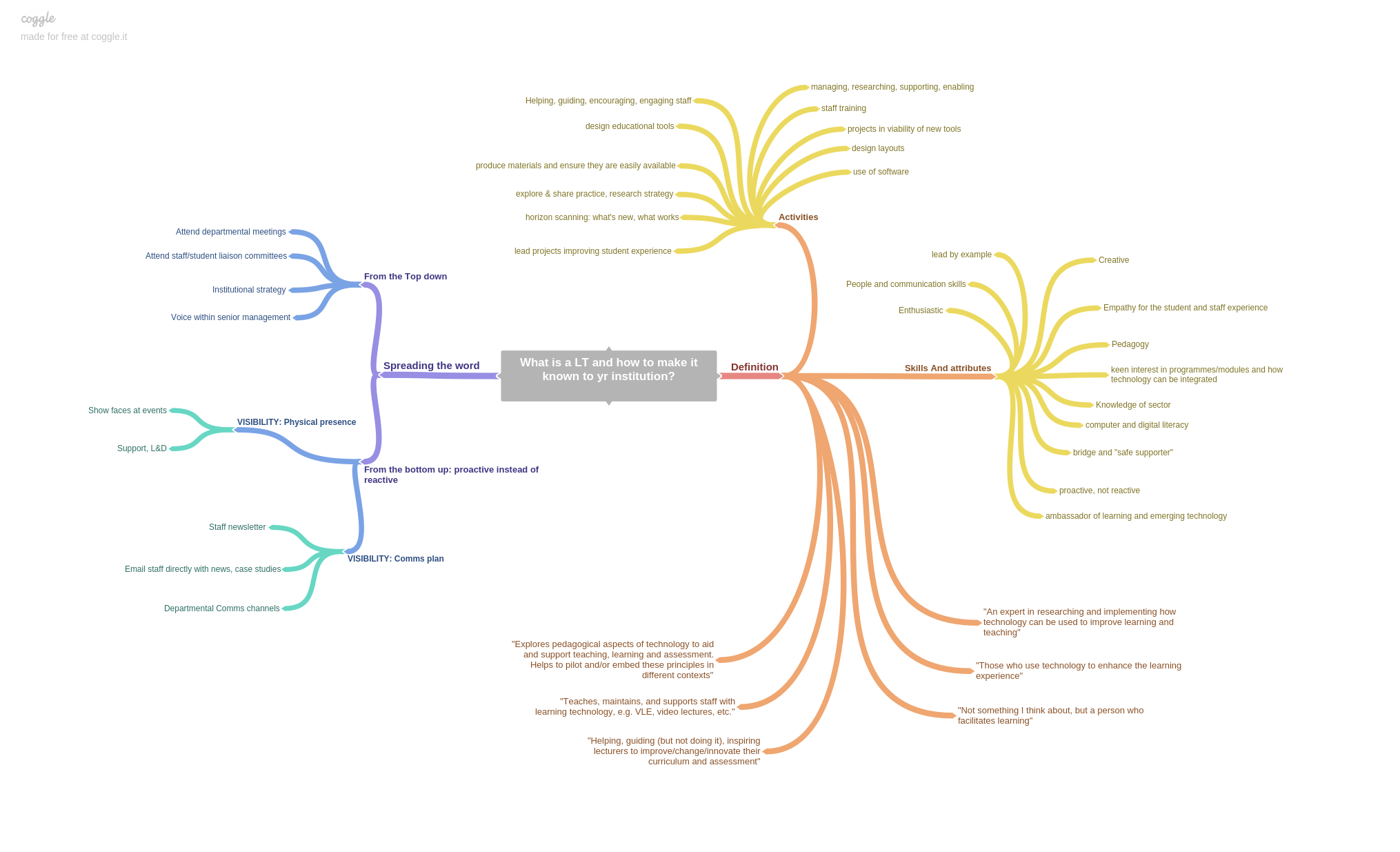
LTI in the spotlight
Last week staff from LTI attended the Association for Learning Technology’s annual conference (ALT-C 2016). It was an eventful three days at the University of Warwick for the team, with five of us presenting a total of 4 papers and one keynote. And oh, we also won the Learning Technologist of the Year Awards!
Learning experiences and virtual learning environments: It’s all about design!
A design for learning; Learning Experiences for the Post-Digital World – Peter Bryant
In the first part of his presentation, Peter described his new approach to teaching and learning whereby seven learning experiences (found, making, identity, play, discontinuity, authenticity and community) can “shape, influence and enhance the opportunities for students to learn, to share learning and to teach others in a post-digital world”. Participants then discussed how existing learning technology tools could be used to create such learning experiences.
You can find a summary, reflections and slides from Peter’s presentation on his blog
Good post: we’re not using technology to its full potential. We’re using it to do old things in new ways. https://t.co/PO4vgXe831
— Tony Burke (@TonyBurke1) September 9, 2016
Innovating from the Outside In: a Creative Hub to Change eLearning Practice- Sonja Grussendorf
Sonja introduced the audience to LTI’s “creative hub”, a project bringing together film makers, artists and designers, and how it is being used to design a VLE that can “accentuate communication between participants; support independent learning, collaboration and student creativity; facilitate peer learning and peer assessment and deliver ongoing, two-way feedback opportunities.”
very well thought out and presented session from @authenticdasein #altc
— Sheila MacNeill (@sheilmcn) September 8, 2016
Physical teaching and learning spaces
Learning Spaces: Roles and Responsibilities of the Learning Technologist – Kris Roger and Sarah Ney
While Sonja was presenting on virtual spaces, Kris and myself discussed physical teaching and learning spaces. More specifically, we reflected on a recent project to develop new active learning spaces at the LSE that made us wonder about what our roles and responsibilities as learning technologists were in the design of learning spaces.
Thought-provoking presentation by @KrisEdTech & @SarahNeyLTI#WhatIsSpace#WhereDoWeLearn#altc
— Elaine Brown (@ElaineBrownARU) September 8, 2016
Copyright and eLearning: who else but Jane Secker?
Jane presented a paper AND a keynote at ALT-C this year!
 Lecture Capture: Risky Business or Evolving Open Practice? co-presented with Chris Morrisson, Copyright Licensing and Compliance Officer at the University of Kent.
Lecture Capture: Risky Business or Evolving Open Practice? co-presented with Chris Morrisson, Copyright Licensing and Compliance Officer at the University of Kent.
Jane and Chris presented the findings from a recent survey on institutional attitudes towards intellectual property issues in relation to lecture capture and contents used in lectures. They also reflected on the relation between good policy and good practice and how to support staff in implementing and encouraging it.
Keynote: Copyright and eLearning: Understanding our Privileges and Freedoms
Jane presented an entertaining, fun, moving and very interesting keynote on how a better understanding of copyright can empower copyright users and educators.
You can view Jane’s full keynote on youtube:
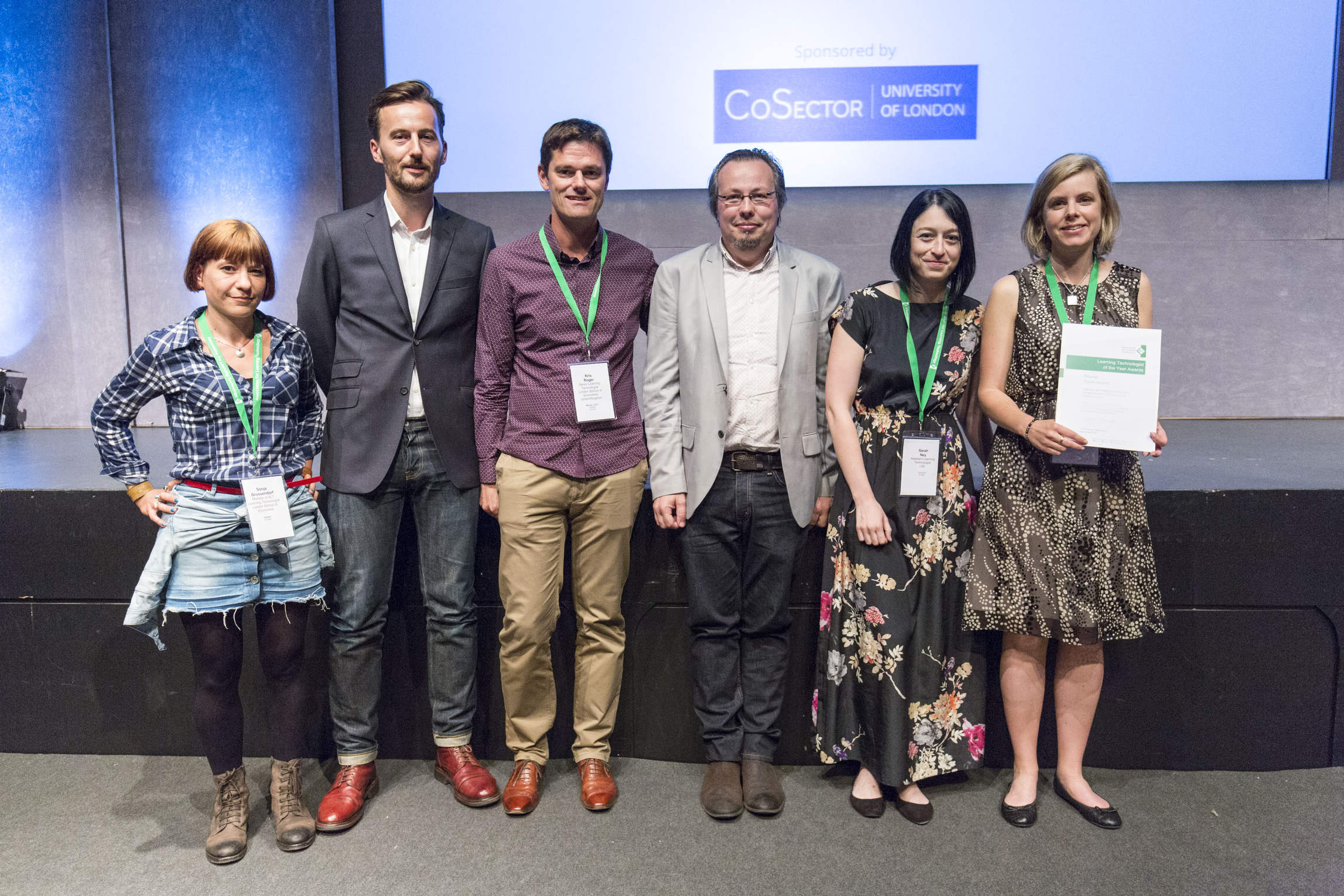
Last But Not Least: We won!
LTI was presented with the prestigious Team Learning Technologist of the Year Award last Wednesday for their work around Students as Producers. The award recognises “outstanding achievements in the learning technology field and the promotion of intelligent use of Learning Technology on a national scale”.
“LSE are proud to be selected as the Learning Technology team of the year, especially in its 10th year. This recognition by our peers is a celebration of the innovative work being done by academic and LTI staff to better the student experience and provide more opportunities for engaging, positive and transformational education with technology.” Peter Bryant, Head of LTI
Here are a few pictures from the evening:










 As part of the Urban Policy and Planning course, students produce written work alongside a group presentation and a short interpretive film of neighbourhood fieldwork. Film-making started two years ago with students using their own devices. Last year they were helped by an LSE alumnus who is now a filmmaker to better understand the process of storytelling and how to use the equipment. This year, Nancy applied for DSLR kits to improve the quality of the work produced. An evening screening of the 8 short films produced by the project groups was also organised at the LSE, at the end of which a panel of ethnographers and filmmakers judged the films and awarded three prizes: Best Overall Film, Best Cinematography and Judges Choice.
As part of the Urban Policy and Planning course, students produce written work alongside a group presentation and a short interpretive film of neighbourhood fieldwork. Film-making started two years ago with students using their own devices. Last year they were helped by an LSE alumnus who is now a filmmaker to better understand the process of storytelling and how to use the equipment. This year, Nancy applied for DSLR kits to improve the quality of the work produced. An evening screening of the 8 short films produced by the project groups was also organised at the LSE, at the end of which a panel of ethnographers and filmmakers judged the films and awarded three prizes: Best Overall Film, Best Cinematography and Judges Choice.
 As highlighted in the description of the project, video production was gradually introduced in the Geography course. Students received the help from a professional filmmaker and were able to familiarise themselves with the equipment during a trip to Manchester in the first part of the year.
As highlighted in the description of the project, video production was gradually introduced in the Geography course. Students received the help from a professional filmmaker and were able to familiarise themselves with the equipment during a trip to Manchester in the first part of the year.


 In the spring of 2015 I finished my first year of American grad school. Coming from the German university system I knew it was going to be a Protestant re-education camp in terms of work load and ethic. By the end of that spring I had to write three sizeable papers in short succession and ‘time is of the essence’ took on a new meaning. Lucky for me some of my friends had just started using this writing set-up that streamlines all the things that take no brain but lots of time: citations, the bibliography, and worrying about the different format of citations when in footnotes vs. when in the bibliography.
In the spring of 2015 I finished my first year of American grad school. Coming from the German university system I knew it was going to be a Protestant re-education camp in terms of work load and ethic. By the end of that spring I had to write three sizeable papers in short succession and ‘time is of the essence’ took on a new meaning. Lucky for me some of my friends had just started using this writing set-up that streamlines all the things that take no brain but lots of time: citations, the bibliography, and worrying about the different format of citations when in footnotes vs. when in the bibliography.








