
The UK is largely seen as a ‘service-based’ economy, which means that services – such as financial, legal, research & development (R&D), real estate and so on – account for the bulk of economic output and employment. Manufacturing, on the other hand, only formally accounts for around 10% of the economy and 9% of employment.
However, manufacturing’s importance for the UK economy far outstrips its relatively small size. Manufacturing accounts for a disproportionate share of total exports (45%), wages in manufacturing are around 15% higher than the national average, and manufacturing accounts for 65% of private sector R&D spending. Several manufacturing sectors also have high productivity as figure 1 shows. Also, some services exist largely because they are closely tied to manufacturing (such as industrial R&D and service jobs in the repair of industrial machinery).
Figure 1. Manufacturing sectors are typically more productive
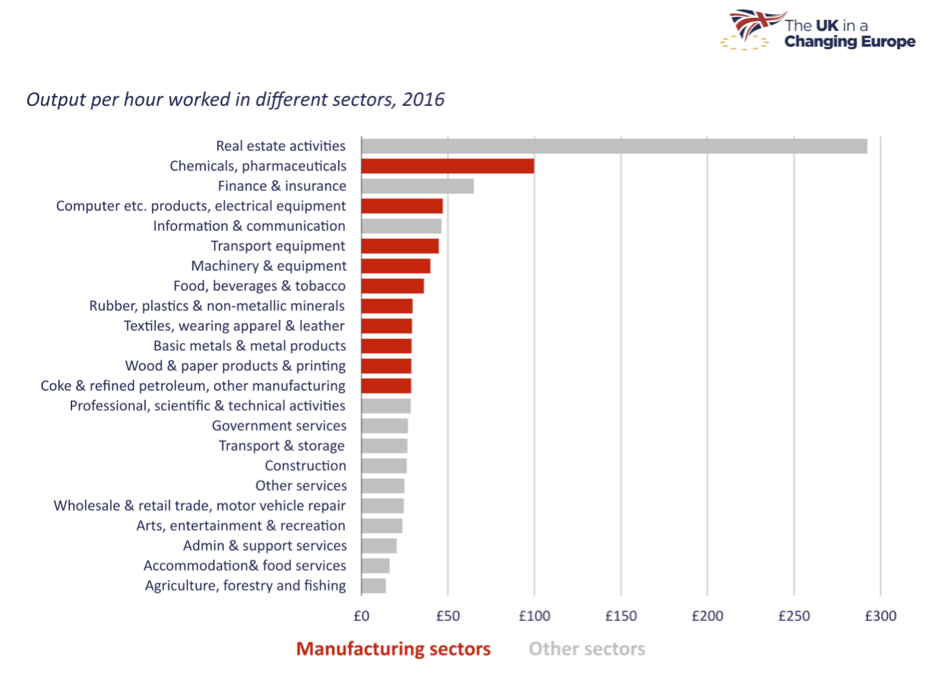
Source: Office for National Statistics, LPROD01, 2016
Taking such links into account, manufacturing is actually responsible for 15-22% of the economy and 18-27% of employment in the UK (see figure 2). Given this, it’s fair to say that shocks to UK manufacturing can have a major impact on the broader UK economy.
Figure 2. Manufacturing in the UK economy
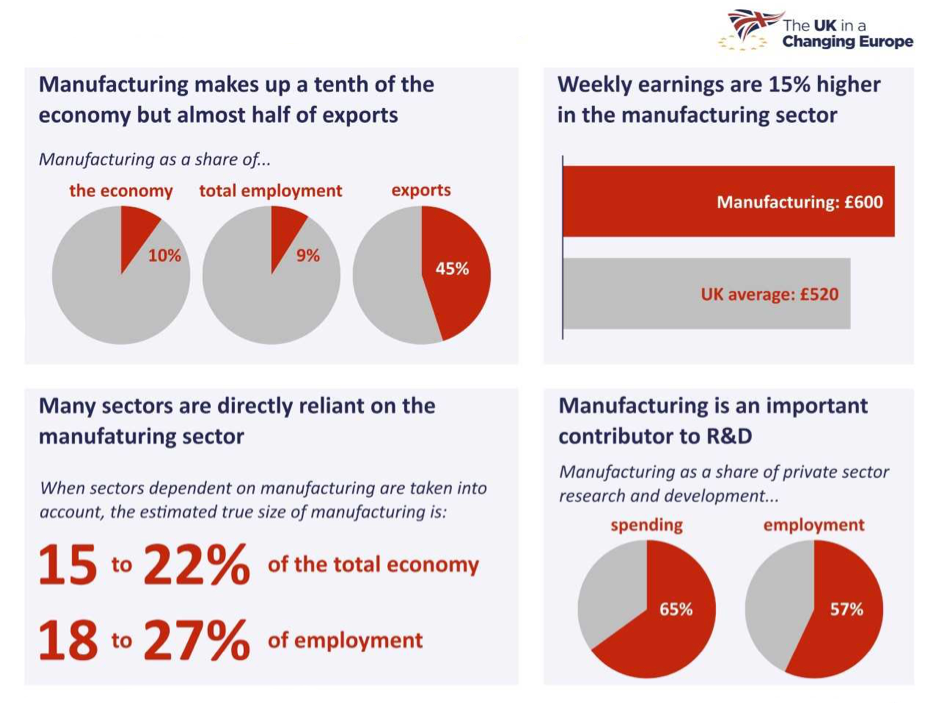
Source: Office for National Statistics, EMP13: All in employment by industry, 2018; Regional gross value added (balanced) by industry, 2018; Office for National Statistics, BPAN, 1KBH, 2018; Office for National Statistics, EARN02: Average weekly earnings by sector, 2018; University of Cambridge Institute for Manufacturing, Inside the black box of manufacturing: Conceptualising and counting manufacturing in the economy, 2019; Office for National Statistics, Business enterprise research and development, 2018.
Manufacturing has close links with the EU
UK manufacturing is tightly linked with the EU in a number of ways. Nearly a half of UK exports and imports of manufactured goods go to, and come from, the EU, and EU labour helps fill key skills gaps in the UK. Some sectors, like automotive, are highly integrated into EU-wide supply chains.
Intermediate goods (such as car parts or semi-finished products such as steel bars) often criss-cross the borders of various EU countries (and also the UK) multiple times, as they are shipped from factory to factory to undergo various industrial processes, before being assembled into final products. The latter in turn could be sold in any EU country.
In many cases, sectors such as automotive or chemicals need such intermediate goods delivered ‘just-in-time’ to save on the costs of stockpiling. They will often hold very low stocks of these goods, sometimes enough for just a few hours of production, and rely on multiple daily deliveries within tight time slots, sometimes as short as 15min. Disruptions of links with the EU after the transition period ends, such as through customs delays, could therefore have a negative effect on manufacturing companies in the UK.
Brexit impact on manufacturing
In a new report on manufacturing, we have reviewed existing evidence on what effects Brexit will have on the UK manufacturing sector, covering ten key areas: tariffs, rules of origin, non-tariff barriers, regulatory alignment, geographical indications, data protection, state aid, skills, research & development, and uncertainty & investment. Overall, the evidence, including the opinions of most manufacturers, is that the effects will be disruptive and negative. However, the extent to which this will be the case will crucially depend on the outcome of the Brexit negotiations.
A worst case scenario for manufacturing would be one in which there is no trade deal between the EU and the UK. This would introduce delays at the UK-EU border, add costs (such as tariffs, the need for separate safety certifications in the UK and the EU, etc.) and disrupt exactly the sort of links described above – such as tightly interwoven supply chains. If this happens, then manufacturing in general will be negatively impacted, and some manufacturing sectors, such as volume automotive production will be badly affected in particular, especially at a time when they are recovering still from the impact of Covid-19.
However, even with a free trade agreement, a degree of disruption would still occur. For example, manufacturers feel that is important to ensure that UK and EU technical, safety, and other regulations remain aligned. If they do not, and if there is no agreement on the mutual recognition of standards, manufacturers will be forced to make products to different specifications for the UK and EU markets and do safety and other tests twice. This would add to the costs of doing business, with industry saying that there would be no discernible benefit from this.
Another big challenge for manufacturing is uncertainty around Brexit – just six months until the transition period ends, it is still unclear what will happen in many areas. Trade and regulation that we mention above are just two such areas, but industry simply does not know yet how data protection will work, whether and how they will still be able to employ EU staff for short periods of time, how state support for manufacturers will function, and so on.
Uncertainty is one of the biggest detriments to investment, which has already taken a hit. For example, investment has fallen considerably in recent years in the automotive industry, one of the biggest sectors of UK manufacturing, and major investment decisions such as that by Peugeot in its Vauxhall plant at Ellesmere Port, are effectively on hold.
Policy reset?
UK manufacturing may need to be cushioned from the impacts of Brexit, and this might become particularly necessary in light of the economic impact of the Covid-19 lockdown. Measures taken to support businesses during the lockdown, such as wage support and loans, could be reactivated along with measures such as tax deferrals.
Longer term, a more active policy could also be considered post-Brexit. A carefully integrated set of policies (aimed at boosting skills, innovation, and technology adoption, providing finance and so on) could be targeted at specific industrial sectors to support their long-term competitiveness and help them in recovering from the impact of Covid-19.
This could be combined with a drive towards take up of industry 4.0 technologies (where other countries have gone further than the UK) and embracing environmental sustainability, for example, by paying particular attention to supporting the adoption of green technologies. And more power and funding could also be given to the UK’s countries and regions, so they can set their own industrial goals (in coordination with the central government).
So whatever the exact form of Brexit at the end of the transition period, a new industrial policy could help in both dealing with Covid-19 and Brexit challenges and embracing new opportunities such as Industry 4.0 technologies. That would require something of a ‘policy reset’ moment on the part of government when it comes to industry and industrial policy.
♣♣♣
Notes:
- This blog post is based on the report ‘Manufacturing and Brexit’.
- expresses the views of its author(s), not the position of LSE Business Review or the London School of Economics.
- Featured image by WorldSkills UK, under a CC-BY-2.0 licence
- When you leave a comment, you’re agreeing to our Comment Policy
 David Bailey is professor of business economics at the Birmingham Business School, and a Senior Fellow of the ESRC’s UK in a Changing Europe programme, exploring the impacts of Brexit on UK automotive and manufacturing. He has written extensively on industrial and regional policy, especially in relation to manufacturing and the auto industry. He has been involved in a number of recent major projects including the recent Horizon2020 RISE project MAKERS where he led the Work Package on Industrial Policy. He is Editor-in-Chief of the leading journal Regional Studies and Chair of the RSA Europe Think-Tank and policy forum. His latest co-edited book ‘Keeping the Wheels on the Road. UK Auto after Brexit’ has recently been published by Bite-Sized Books. David is a regular media commenter and newspaper columnist. Tweet him @dgbailey
David Bailey is professor of business economics at the Birmingham Business School, and a Senior Fellow of the ESRC’s UK in a Changing Europe programme, exploring the impacts of Brexit on UK automotive and manufacturing. He has written extensively on industrial and regional policy, especially in relation to manufacturing and the auto industry. He has been involved in a number of recent major projects including the recent Horizon2020 RISE project MAKERS where he led the Work Package on Industrial Policy. He is Editor-in-Chief of the leading journal Regional Studies and Chair of the RSA Europe Think-Tank and policy forum. His latest co-edited book ‘Keeping the Wheels on the Road. UK Auto after Brexit’ has recently been published by Bite-Sized Books. David is a regular media commenter and newspaper columnist. Tweet him @dgbailey
 Ivan Rajic works at the Birmingham Business School and is funded by the ESRC’s UK in a Changing Europe programme.
Ivan Rajic works at the Birmingham Business School and is funded by the ESRC’s UK in a Changing Europe programme.






We forget how Britain became Great. MANUFACTURING. Sadly as commented, this only reflects less than 20% of our economy. Forget politics. The UK is an accident happening and requires turnaround. We are reliant on property value growth rather than actually making ‘REAL’ money. Sadly, the past years have allowed service industries to grow. A culture of moving paper around provides no future. Now that Brexit is done, it shall be interesting how the economy, especially London survives. Manufacturing is what we need. We have been worries about Europe and how it affects the UK. Go over the channel, Look at how manufacturers over there are panicking but not reported. The Chancellors needs to look at the new UK after the pandemic, Steady the ship and get back to making REAL money.
Like what John says in above comment. Us British have always been great at manufacturing.
It’s critical for us to build up our manufacturing again in order to create true wealth.
Past governments have focused on services but this is all propped up indirectly by manufacturing.