 The options for decolonising Puerto Rico have always been complex and contested. But the US decision to force a “status quo” option on to the latest ballot has undermined this chance to settle the issue once and for all, writes Gibrán Cruz Martínez.
The options for decolonising Puerto Rico have always been complex and contested. But the US decision to force a “status quo” option on to the latest ballot has undermined this chance to settle the issue once and for all, writes Gibrán Cruz Martínez.
Amid a debt crisis, mass mobilisations, and anti-austerity strikes, in June 2017 voters in Puerto Rico will be asked to vote in their fifth non-binding referendum on the political status of the islands. Initially billed as an inevitable end to US colonialism, with a clear choice between full US statehood and different forms of sovereign control, the US State Department has since forced a status quo option on to the ballot. So what exactly is the current status of Puerto Rico? What options are on the table and how do they differ from previous votes? And what is at stake for this most neglected of Latin American countries?
The unacknowledged colony: Puerto Rico’s current status
Puerto Rico has been an “unincorporated territory” of the United States since 1898. Puerto Ricans have been US citizens since 1917, yet they have no voting representatives in Congress, nor do they have the right to vote for the US President. Since 1952, Puerto Rico has had the official title of Commonwealth of Puerto Rico or Free Associated State. This represents a colonial status for some and a “mutually agreed association” between two sovereign countries for others.
However, the US has repeatedly confirmed the colonial status of Puerto Rico. In 2016 the three branches of the US government confirmed that Puerto Rico is not sovereign and is subjected to US Congress, revealing the lack of political and juridical sovereignty in Puerto Rico. Congress then appointed an unelected financial control board, which not only imposed an austerity programme in late 2016, but also took control of legislation enacted by the elected government, arguing that all new law must be consistent with the board’s Fiscal Plan.
The US Congressional Research Service acknowledged that: “Although the Constitution of 1952 provides for self-government by Puerto Ricans, Congress ceded none of its own plenary authority over the islands.” This makes the 1953 approval of UN Resolution 748, which removed Puerto Rico from the list of non-self-governing territories, seem a little disingenuous. Indeed, the UN Decolonization Committee itself has passed 35 resolutions calling upon United States government to expedite a self-determination process for Puerto Rico.
The many faces of Puerto Rican sovereignty: options past and present
Puerto Rican governments have held four referendums on political status since 1967, but the US Congress has endorsed none of these despite being the only stakeholder with the power to resolve the colonial status of Puerto Rico. The options to date have been as follows:

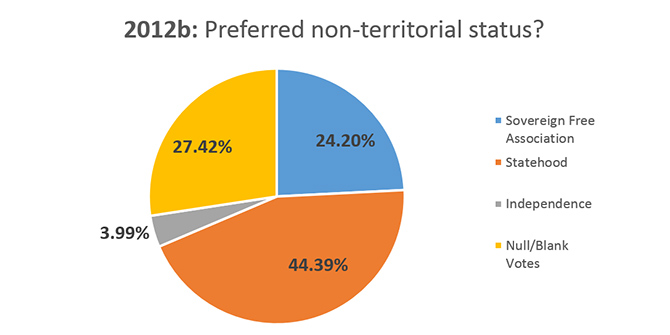
The Free Associated State option was favoured in the first two referendums (1967 and 1993). In 1998 the pro-statehood Party boldly added an extra option in the hope of dividing status-quo voters, but ultimately it was “none of the above” which won out with 50.3%. In 2012, most electors voted to change the current territorial status, and in the second ballot statehood was the preferred non-colonial option, though it received less than 50% of the vote (see below, and click for charts of every referendum since 1967).
Results of 2012 political status referendum
Between statehood, sovereignty, and the status quo: the options on 11 June, 2017
Option 1: Statehood
Integration of a non-sovereign territory (i.e. Puerto Rico) into a sovereign state (i.e. US) is one of the decolonising options recognised by the United Nations. After integration, peoples of both territories should have equal rights and responsibilities, equal citizenship, and equal opportunities for political participation in all branches of government.
Advocates of statehood argue that this is the only non-colonial status that guarantees the US citizenship and a permanent status with the US. Moreover, Puerto Rico would gain representation in Congress and the right to vote for the head of state. There would be equal access to social assistance and social security benefits, whereas now Puerto Ricans contribute to Medicare but are not entitled to receive Supplemental Security Income in old age. Statehood advocates also argue that the political stability of the US will bring more inward investment. In January, the non-voting US congressional representative for Puerto Rico introduced the Puerto Rico Admission Act, which proposes 3 January 2025 as the date of incorporation if statehood is chosen.
But for this to happen, Congress would have to accept the incorporation of a Spanish-speaking Latin American country during the xenophobic administration of Donald Trump. Not only would this new state come with an unsustainable debt of around US$70 billion, it would have more representation in Congress than many less densely populated states. This would require US$2.3 billion in new federal taxes according to a US Government Accountability Office report.
Public opinion appears to remain split, but the governor of Puerto Rico, Ricardo Rosselló, will consider a majority for statehood on 11 June as a mandate to pursue the unilateral “Tennessee Plan” followed by Tennessee, Michigan, Iowa, California, Oregon, Kansas and Alaska to become states of the US.
Option 2a: Sovereignty via Independence
The identity argument for independence is simple: Puerto Rico is a Latin American nation with its own language and traditions, which can only be retained by avoiding annexation to the United States. The economic argument, meanwhile, is based on political power. The Independence Party has said it will use this power to integrate Puerto Rico in the global economy by creating bilateral and multilateral agreements, joining regional and global organisations (such as the UN, the Caribbean Community, and the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States), and using monetary policy to control inflation and promote investment. Imported goods are expected to become up to 30% cheaper with the abolition of Cabotage Laws that oblige Puerto Rico to use the US Merchant Marine for trade with the US, costing the Puerto Rican economy some US$ 29 billion from 1970 to 2012. Advocates of independence argue that electoral support for independence has been decimated throughout the last century by US and local repression of “independentistas” and “manufacturing of consent” through consistently linking independence to poverty and communism.
According to the United Nations, free association is another option for the decolonisation of non-sovereign territories under international law. If Puerto Rico takes this path, it will become a sovereign state with a free and voluntary association with the United States.
The main divergence from the current status is that free association would not subordinate Puerto Rico to control by the US Congress. This is instead a relationship between sovereign states, with established legal agreements connecting them in whichever policy areas they choose, whether political, economic, military, or any other. The Republic of Palau, the Federated States of Micronesia, and the Republic of the Marshall Islands utilise free association with the United States, with the US offering economic and social assistance in exchange for hosting of US military bases. Both sides benefit permit free movement of people between their territories.
The Sovereign Union Movement (MUS), a political party supporting free association, highlights dual citizenship, freedom of movement for people and goods, and continuation of US social security entitlement as significant benefits. The MUS also argue that Puerto Rico would be able to claim reparations for damage suffered during colonial subordination and for violations of human rights. The free association pact would be signed by both sovereign states and could be terminated unilaterally by either party.
Option 3: Status quo
The current territorial status of “Free Associated State” is the only option that perpetuates colonial power of the US over Puerto Rico. Puerto Rico would remain subordinated to the powers of the US Congress and subject to the Territory Clause of the US Constitution.
The Popular Democratic Party embodies the defence of the status quo, which they consider the ‘best of both worlds’. This status combines some characteristics of a sovereign country (separate language, culture, and national representation in sports events) with other benefits of a permanent union with the US (citizenship and free trade). They advocate an updated version of the current territorial status called the enhanced Free Associated State, whereby Puerto Rico receives the greatest degree of autonomy possible within this permanent relationship with the US. Ultimately, however, even an enhanced version would imply colonial status and subordination to the US Congress.
The malign effects of US arm-twisting on the status quo option
Since the US State Department demanded inclusion of a status quo option, calls to boycott the referendum have grown. Indeed, the Popular Democratic Party, the Independence Party, and the multiparty coalition supporting free association have opted not to participate in the referendum. The Popular Democratic Party argues that the status quo option undermines their view of an enhanced Free Associated State. Supporters of the sovereign options, meanwhile, refuse to participate in a referendum that includes an extension of the current status.
If the referendum does go ahead on 11 June 2017, it will represent just another missed opportunity. This will be the fifth time in 50 years that Puerto Ricans go to the polls in a non-binding process. If the idea of the referendum is to resolve Puerto Rico’s territorial status, why include the status quo as a viable option? If the US Congress had had genuinely wanted to decolonise Puerto Rico, they would have sat down long ago with political parties and social movements to establish a set of non-colonial options for inclusion in a binding referendum, but its actions instead show disdain for the idea of ending colonialism in Puerto Rico.
International pressure is needed to finally end colonialism, not only in the Caribbean but also in the remaining non-self-governing territories of the world. In Puerto Rico national mobilisation is required to show the world that a majority of Puerto Ricans demand immediate decolonisation, irrespective of the precise form that it may take, for this is the choice that has just been stolen from them.
This article originally appeared on the Latin America and Caribbean Blog.
“Banderas de Puerto Rico y USA ondeando” by Arturo de la Barrera is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0
Please read our comments policy before commenting.
Note: This article gives the views of the author, and not the position of USAPP – American Politics and Policy, nor of the London School of Economics.
Shortened URL for this post: http://bit.ly/2pGT0hl
________________________________
 Gibrán Cruz Martínez – University of Agder
Gibrán Cruz Martínez – University of Agder
Dr. Gibrán Cruz Martínez is a Postdoctoral Research Fellow at the University of Agder, Norway, where he teaches Introduction to Latin American Studies. His comparative research focuses on social welfare policies, multidimensional poverty, and inequality in Latin America and the Caribbean. His current research projects explore (i) how economic policies, globalisation and forms of political mobilisation shape welfare systems in Latin America, and (ii) the affordability and sustainability of universal social pensions. He is also an Editorial Board member of the Latin American critical development blog and journal Alternautas.




This analysis, like others on the subject, tries too hard to paint the Puerto Rican public as victims of U.S. federal policy. Yet the cry for independence is waning. It should be noted that Puerto Rico’s:
— citizens are free to relocate and take up work anywhere within the United States
— citizens do not pay federal taxes, but the territory receives a net significant influx of U.S. federal dollars
— better off economically than independent nations in the region
— importance to the military has vanquished in the modern era
Examples in this article that point to alleged unfairness fail to mention the fact that the residents ask for handout programs, but do not pay into them (e.g. SSI is funded U.S. taxpayers, not Puerto Ricans and via Medicare).
If Puerto Ricans are looking for targets to blame for their situation, they should focus internally instead of fashioning strained arguments about neocolonialism. Look no further than the Government Development Bank of Puerto Rico, government service workers unions, and the island’s own corrupt politicians first. Requests for more U.S. federal handouts has worn thin–and now that Puerto Rico lacks any military significance, the willingness for those living in the 50 states to pay for its borrow, bribe, and overspend governmental ways has waned.
The diaspora of Puerto Rico citizens to Florida, New York and elsewhere is not unlike what happens within the 50 states when a region’s economy and governmental stability break down. If an independent Puerto Rico were actually desired by a majority of its citizens, many living to the north would be all for it. In the meantime, allegations that Uncle Sam is primarily to blame for all ills of the past half century is simply myopic.
Dear Jay,
Thanks for the comment. Let me clear out some points:
1. I am not trying “to paint the Puerto Rican public as victims of U.S. federal policy”. But to clear out the different non-colonial options that Puerto Rico have. And yes, non-colonial because Puerto Rico is still a colonial non-self-governing territory of the US. In my personal opinion, the existence of colonies in the XXI century is inexcusable.
2. “citizens are free to relocate and take up work anywhere within the United States”: Yes indeed, since 1917 US citizenship was imposed on all Puerto Rican citizens (as I mentioned). Now, US citizens residing in Puerto Rico do not have the same rights or responsibilities as any other US citizens residing in the 50 states.
3. “citizens do not pay federal taxes, but the territory receives a net significant influx of U.S. federal dollars”: This is false, Puerto Ricans pay federal taxes (including payroll taxes, income/export taxes and others). Puerto Ricans are not required to file federal income tax, with a few exceptions (please read here: https://www.irs.gov/taxtopics/tc901.html).
4. “the territory receives a net significant influx of U.S. federal dollars”. Yes, this is true, in 2014 Puerto Rico received 17 billion of US federal transfers. Now we have to make a distinction between contributory benefits (benefits received as a result of tax-payment or service provided) and granted benefits (benefits transferred without contributions or service). 77% of the US federal transfers to Puerto Rico are contributory benefits, which residents of Puerto Rico receive after meeting the eligibility requirements (social security, medicare, military pensions, etc.). In addition, it is important to also take into account the over 20 billion/year Puerto Rico imports from the US in consumption goods, and the over 30 billion/year US corporations repatriate in capital gains.
5. “better off economically than independent nations in the region”, in terms of GDP per capita YES. But I invite you to take a look at the income inequality levels and the poverty levels. And please compare those indicators to Latin American countries, but also to the 50 US states.
6. “Examples in this article that point to alleged unfairness fail to mention the fact that the residents ask for handout programs, but do not pay into them (e.g. SSI is funded U.S. taxpayers, not Puerto Ricans and via Medicare).” This is false, please read point number 4.
7. “If Puerto Ricans are looking for targets to blame for their situation, they should focus internally instead of fashioning strained arguments about neocolonialism.” There is no doubt that the Puerto Rican governments are one of the main (if not the main) responsible for the actual economic crisis. But using your own words, it would be ” simply myopic” not to consider the role of colonialism in Puerto Rico’s crisis.
Again, the aim of this article is not to explain Puerto Rico’s crisis, but to present the different non-colonial options available and to criticize the colonial status of Puerto Rico.
Thanks for reading the article and apologies for the late reply, I just saw your comment.