 How much inappropriate content are children encountering on YouTube? With a huge amount of content uploaded each minute, YouTube’s content regulations can be less rigorous than those of conventional TV broadcasters, and the format to complain about content is not always obvious. In this post, David R Brake outlines some suggestions for policy change, user interface, and advice for parents on these YouTube problems. David is an alumnus of the Media department at LSE and his research interests include digital divides and digital media literacy, privacy in online contexts, mediated interpersonal interaction, the political economy of the social web and other internet applications, online journalism and the interconnections between new media, the mass medias and politics. [Header image credit: Paul, CC BY-SA 2.0]
How much inappropriate content are children encountering on YouTube? With a huge amount of content uploaded each minute, YouTube’s content regulations can be less rigorous than those of conventional TV broadcasters, and the format to complain about content is not always obvious. In this post, David R Brake outlines some suggestions for policy change, user interface, and advice for parents on these YouTube problems. David is an alumnus of the Media department at LSE and his research interests include digital divides and digital media literacy, privacy in online contexts, mediated interpersonal interaction, the political economy of the social web and other internet applications, online journalism and the interconnections between new media, the mass medias and politics. [Header image credit: Paul, CC BY-SA 2.0]
In recent weeks parents have been shaken by media reports about upsetting, offensive or crassly commercial videos that children using YouTube and YouTube Kids could be exposed to just by following links from content they are familiar with.
Some examples include Peppa Pig eating her father or being tortured at the dentist.
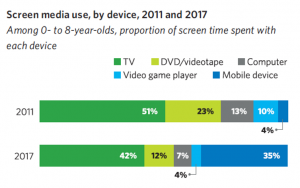
While most of the time that kids spend watching screens is still conventional TV, a recent report from Common Sense Media shows children’s use of phones and tablets in the United States has exploded in the last few years.
Because the screens are smaller and kids may be wearing headphones it is harder for parents to be aware of what their kids may be watching, and they may not fully appreciate the difference in the level of child protection provided by broadcast TV and YouTube.
YouTube regulates itself
Children’s broadcasters source their programs from a limited pool of providers and are expected to carefully approve every program they air — if they show inappropriate material they can be fined or even lose their licence to broadcast.
YouTube largely regulates itself. Since 400 hours of video is uploaded to the service every minute, it relies heavily on uploaders to label their work appropriately. YouTube also uses computer programs to try to identify and classify problematic content, and complaints by users themselves.
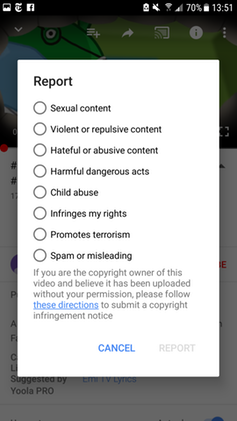
This last idea — of user complaints — depends on parents to be vigilant or to teach children to make these complaints themselves. But there is no prominent complaint option in YouTube’s interface. The option to report harmful content is hidden in a sub-menu with a flag as a rather subtle visual cue.
YouTube’s global head of family and learning content, Malik Ducard, maintains that “less than .005 per cent of the millions of videos viewed on YouTube Kids in the past 30 days had inappropriate content.” But this low number may largely reflect under-reporting of problems. It also does not take into account the sizeable number of children using “regular” YouTube (as opposed to YouTube Kids).
When kids across Europe were asked in 2010 about what bothers them most online, one in six said video-sharing sites — a higher proportion than social media or websites in general. And this was before the recent increases in children’s use of YouTube.
Although this video was highlighted in at least one major news outlet as problematic, the content is still available on YouTube and because of its image, appears ‘family friendly.’
Changes are needed to guidelines
Google (which owns YouTube) has responded to this criticism with a five point plan. They have promised “tougher and faster application of community guidelines” and say they plan to raise the number of people monitoring content to 10,000 in 2018 which is a 25 per cent increase.
This is a step in the right direction. However, we don’t know enough about the scale of the problem to know whether this will be adequate. Also, at least one of the “answers” offered in their recent announcement seems a retrograde step.
They have repeated their promise which they announced in June: They will be removing ads from any content “depicting family entertainment characters engaged in violent, offensive or otherwise inappropriate behaviour, even if done for comedic or satirical purposes.”
There is a place for satirical content aimed at adults – if it can be identified in order to remove ads from it why not just segregate it away from childrens’ content instead? This move by Google seems more an attempt to appease nervous advertisers than a child protection measure.
Fortunately, one of the measures they have announced is that they will be “engaging and learning from experts.” In that spirit, I have provided below some recommended policy and interface changes which I believe Google should consider.
I also offer some practical suggestions which, if implemented, may help parents navigate YouTube. As someone who has studied digital media literacy for the past decade, I believe they could go some way towards helping families cope better.
Recommended policy changes
- Share how its content sorting technology (“algorithm”) works with a panel of third party scholars and policy experts to make sure it works as it should.
- Conduct regular random surveys to find bad content that has not been reported or automatically filtered out, so that we have some idea of the scale of un-reported problems.
- Publish figures on how well the algorithms are working and how satisfied users are with the decisions made by Google’s staff when they intervene, and provide targets for improvement.
User interface suggestions
- Make the interface easier and more obvious for parents and children to report problematic YouTube content.
- Take greater steps to make YouTube Kids more appealing to a wider range of children, including older ones, in order to prevent them from going to the more dangerous You Tube (for adults). At the moment, it is not available on computers and it only differentiates between pre-school and school-age children. In practice this likely means kids older than eight will find it unappealing. Several ‘levels’ of YouTube Kids – pre-school, school and teen – would help.
- Make fine-grained age labelling by content producers mandatory and penalise failure to appropriately label. At present uploaders can only indicate a video is for those 18 and older and video flagged this way cannot earn money through advertising, which discourages honest appraisal of content by producers.
- Work harder to ensure that the “show me similar” algorithms they use to select next videos do a better job of segregating adult parody or satirical content from kid-oriented programming.
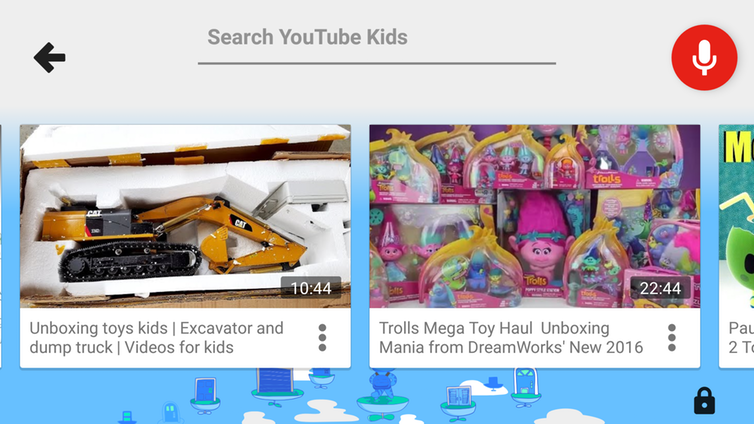
Advice for parents
Because everyone’s experience of YouTube is customised and therefore different, and because YouTube has yet to share much information on the scale of the problems that may exist, it is hard for parents to assess how worried they should be and therefore how they should react. But plenty of video alternatives exist aimed at children.
In Canada for example there are some options: CBC Kids and Treehouse TV, and Radio Canada and Yoopa (in French).
These services may offer a more limited selection than YouTube, but precisely because the content is hand-picked these options are less risky and have potentially a higher proportion of educational as well as entertaining content.
If you do allow your child to use YouTube, warn them that they may find material by accident that is upsetting. Explain it is not their fault they found it and encourage them to talk to you about it if they do see something wrong — or at least show them how to report the problem to Google.
While YouTube Kids provides better “childproofing” than Youtube itself, do not assume it is all harmless
— even if it does not lead to violent content, you might find a greater amount of marketing to children in the guise of entertainment, for example. ‘Channels’ devoted to unwrapping and enthusing about toys given to their authors are popular both on YouTube and YouTube Kids.
Watch with your children from time to time and be prepared to discuss with them the differences between impartial reviews, paid endorsements and advertising — distinctions that even grownups sometimes find difficult to draw!
Lastly, if what you have been reading concerns you, let Google and your elected representatives know.
Governments in particular have tended to allow giants like YouTube and Facebook to regulate themselves, but if they don’t do a better job of it, they may need some outside pressure to do the right thing.
Notes
This text was originally published on The Conversation and has been re-posted with permission.
This post gives the views of the authors and does not represent the position of the LSE Parenting for a Digital Future blog, nor of the London School of Economics and Political Science.





