 What does it really mean to be “right” or “left” in England today? Can we be certain that all who identify as conservative are against immigration? Or can we say that anyone opposing Trident is invariably left? And can we assume that one can never be both pro-immigration and right-wing in economic terms? Jonathan Wheatley explains ideology has a cultural and an economic dimension, and each should be assessed separately. He also argues that for many voters, the terms “left” and “right”, especially in economic terms, don’t mean much.
What does it really mean to be “right” or “left” in England today? Can we be certain that all who identify as conservative are against immigration? Or can we say that anyone opposing Trident is invariably left? And can we assume that one can never be both pro-immigration and right-wing in economic terms? Jonathan Wheatley explains ideology has a cultural and an economic dimension, and each should be assessed separately. He also argues that for many voters, the terms “left” and “right”, especially in economic terms, don’t mean much.
The notions of “left” and “right” have come to define how we understand politics in Western Europe. When it comes to political parties, the consensus in Britain is that UKIP, followed by the Conservatives, take the most right-wing position, while the Greens, SNP and Labour adopt a position furthest to the left. So when a ComRes poll found that the Conservatives were seen by voters as marginally to the right of UKIP, political pundits were shocked.
In ideological terms, the common assumption is that if you are anti-immigration, support an independent nuclear deterrent and adhere to pro-free market economic policies you are right-wing. If you welcome migrants, want to scrap Trident and believe in more state regulation you are left-wing. But as the recent spat between the Institute of Directors and Home Secretary Theresa May demonstrates, pro-business free-marketeers can also be pro-immigration. Conversely, many of those who feel the state should do more to protect their jobs may feel antagonistic towards immigration.
To put these ideas to the test, I draw from data generated by 17,281 England-only users of the WhoGetsMyVoteUK application, launched by researchers from Queen Mary University, London and the University of Zurich (information on methodology included in these papers). Prior to the last general election, users of the application were asked to express their opinions on thirty policy statements, on issues including taxation, welfare, the EU and immigration. Their answers were then matched with the party or parties that best corresponded with those views.
After searching for latent dimensions that may have guided users’ responses (using a technique known as Mokken Scale Analysis), two clear and distinct dimensions were identified. The first is an economic dimension, drawing on issues such as the mansion tax, the bedroom tax, and privatisation of the NHS. The second is a cultural dimension, drawing on issues such as EU membership, immigration, same-sex marriage and English Votes for English Laws. More interestingly, supporters who identified strongly with one or other political party with respect to these dimensions, are separated as much, if not more, by identity-based or cultural issues as by economic issues.
Looking at the position of party supporters with respect to these two dimensions, we see that Conservative supporters stand to the right of the political spectrum in economic terms and Labour and the Greens on the left, as traditionally envisioned. But we also see that UKIP supporters are, in fact, marginally to the left of centre – slightly to the left of Liberal Democrat supporters.
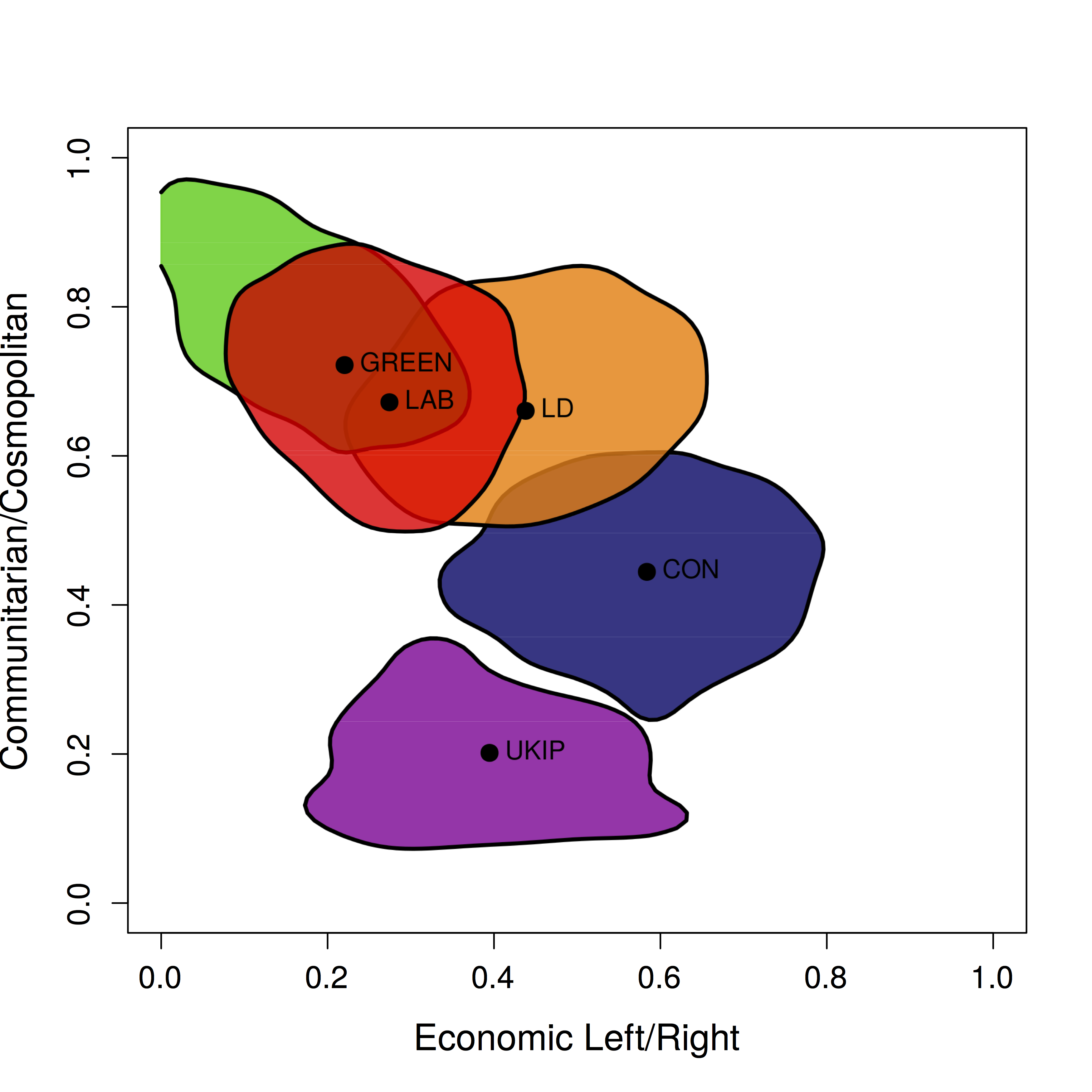
Where UKIP supporters distinguish themselves from other parties is on the cultural dimension. They are, to use David Goodhart’s phrase, far more “communitarian” (i.e. anti-immigration, anti-EU, localist, anti gay marriage and English nationalist) than “cosmopolitan” Green, Labour and Liberal Democrat supporters, while Conservative supporters occupy a “middle-of-the-road” position on the cultural scale. This conforms well to Ford and Goodwin’s characterisation of UKIP as older blue-collar workers who feel threatened by social change and cling to past certainties. In this respect, UKIP is similar to other right-wing populist parties in Europe that draw their support from globalisation’s “losers”.
So what lessons can be learned from these results by party strategists in terms of how best to attract voters? UKIP supporters seem fairly well entrenched near the communitarian pole of an ideological dimension that is unlikely to go away. Yet in economic terms, they are pretty much centrist or even left of centre. This means UKIP must be aware that launching to the right in economic terms, as they did in 2010, is likely to alienate their more economically vulnerable supporters.
At the opposite pole, the Liberal Democrats and the Greens seem to be competing for the cosmopolitan vote, and as small parties it may pay some dividends to portray themselves as more unashamedly internationalist. Given their longer track record and greater experience, the Liberal Democrats seem best equipped to do this. The Greens may be tempted to further consolidate their position on the economic left, but may in time find themselves on the losing side of a turf war with Jeremy Corbyn’s Labour Party. Labour may benefit by occupying a left-of-centre niche economically but moving a bit in the communitarian direction to win back moderate UKIP-ers.
Finally, the Conservative Party risks becoming split between a pro-business, economically right-wing and cosmopolitan wing, and the more socially aware, Eurosceptic and “communitarian” wing led by grassroots organisations. Given the fact that the diagram shows Conservative supporters only slightly to the right of centre in economic terms, following “hard right” free market policies may prove a vote loser.
Evidently, left and right are amorphous concepts that mean different things to different people at different times. Economic leftists are not by definition cosmopolitan and economic rightists are not necessarily communitarian. Interestingly, users’ responses on the cultural dimension were slightly more coherent than those that formed part of the economic scale. Amongst younger, less well-educated and especially less politically interested users, items belonging to the economic scale were barely coherent at all. For these voters, the notions of “left” and “right”, at least in economic terms, are really not meaningful at all.
_______
Note: This article draws on material included in these papers. It represents the views of the author and not the position of the British Politics and Policy blog, nor of the London School of Economics. Please read our comments policy before posting.
 Jonathan Wheatley is Regional Director at the Centre for Research on Direct Democracy in Aarau, Switzerland
Jonathan Wheatley is Regional Director at the Centre for Research on Direct Democracy in Aarau, Switzerland








Might be interesting to run the same data via a Correspondence Analysis. That’d get you underlying dimensions of differentiation more clearly I think.
The words used to describe the vertical axis are, well, the wrong words. Choose a different label for the scale.
interesting research, where would the SNP fit on the diagram?
Ridiculous use of the word communitarian which takes its heritage from notions of the commune. Fascist is the word the author should be using.
Some good stuff in this 2-dimensional system, but it cannot be any good to have ‘communitarian’ be identified as basically unpleasant in the way described here. This bears no connection with the way that many of us (starting with communitarian political philosophers) think of the positive value of the small, the local, of community…
This connects also with what is screamingly missing from this system: the question of being ecological or not, including post-growthist or not. This is the great question of our time.
Being pro immigration is a right wing stance after all it is the company owners and boards that benefit the most from flooding the jobs market and driving down the wages of the workers, not true left winger could possibly be in favour of it.
Agreed entirely, Jonathan. And politics and its typical divide has not and will not solve many of our enduring problems from welfare to banking to immigration to inequality. Changing the system of government will. The system we have is only what we have inherited not a fixture. As you must know, Switzerland has a far better system, but still with major flaws. Anyway, here is what I’m proposing in the form of a Treaty for Government: http://www.treatyforgovernment.com/the-book/ Has anyone a better or different idea of what to do?
Whilst on the left/right labels, does anyone know why the EU’s policy for the free movement of labour, which is classically neoliberal economics and absent of any social considerations, should be supported by the ‘left’ and Labour?
I agree that politics is too complex to be described as left or right
http://politicsismoralpsychology.com/2015/11/05/there-is-no-left-or-right-part-2/
Martin, this is undeniably an example of how much our so-called political servants are disconnected with RREAL people. Further enhanced by the news media also using the terms “left, right and centre” – Not using “right or wrong” to encourage connection and collaboration between public servants and the public.
Shameful, appalling.. and will continue to highlight why politicians simply DO NOT MAKE LIVES BETTER!!!
“Their answers were then matched with the party or parties that best corresponded with those views.” Who did that matching using what criteria?
This question relates to the app itself, rather than the opinion data generated by users, which this article is about. However, to answer the question, it is the app that matches users to parties according to a particular algorithm. The algorithm used is given in Annex 1 of the following article https://ecpr.eu/Filestore/PaperProposal/1afd97c6-2fa7-499b-997f-71824f35b557.pdf. Refer to the “hybrid model”, as this is the one that was used in the WhoGetsMyVoteUK app. In addition, users are presented with a two-dimensional map in which their opinions on a set of issues deemed to belong to two pre-determined dimensions are compared with those of the parties. Parties are coded by experts in an iterative process over two or more rounds of coding. To see how it works from the user’s perspective, go to http://www.whogetsmyvoteuk.com.
Jonathan, this is true. I have also been saying this for a long time now.
Furthermore, if we believe a democratic system to define clearly where Fairness and Justice is key to upholding such principles for ALL, what should clearly follow is a language that is in-tune with what is RIGHT and WRONG – rather a continuation of isolation from politicians and the public – those they are meant to be fully engaged with, listening and understanding, and empowering. One cannot achieve this by speaking two entirely different languages.
Finally, the powerful news media and journalists also have must to bear for this continuation of this political language that disconnects from REAL people – as they too use it.
I am in no doubt that there lies an objective to maintain this “difference” – almost as if protecting the sort of privileges that many of the political and media elites were born into. How, on earth can one explain the reason why it politicians deem it right for immigrants to learn the English language in order to engage, listen and understand the communities they live sin, but politicians themselves continue to isolate themselves with political language of Left, Right and Centre as they continue to allegedly represent their constituents?