Details of forthcoming workshops and links to LTI workshop resources and presentations.
Round the Rotunda: Celebrating Clement House’s New Learning Spaces
LTI is organising a celebration of the new learning spaces in the “rotunda” staircase of Clement House on Wednesday 7th December.
Come join us for coffee/tea, cake and other nibbles and explore the six spaces. It will also be the chance to meet or catch up with the team and what we are up to!
Interested? Book your place
What’s happening on each floor:
Floor 3 – New York

Reception & Food – 3.30pm start
Award-winning LTI
LSE innovators
|
Floor 2 – Rio de Janeiro
Learning Spaces Flipping the Classroom |
Floor 4 – London
Games for Learning
|
| Floor 5 – Sydney
Copyright
|
Floor 6 – Tokyo
Students As Producers Assessment and Feedback |
Save
Mapping learning and teaching
 Our next NetworkED seminar is with James Clay,
Our next NetworkED seminar is with James Clay,
on 23 November 14:30-15:30
James is a Jisc project manager and was previously the Group Director of IT and Learning Technologies at Activate Learning which incorporates City of Oxford College, Banbury & Bicester College and Reading College, where he was responsible for ILT, IT Services, Business Systems and Learning Resources.
We asked James to tell us more about his upcoming seminar on Mapping the teaching and learning
“Mapping is an useful exercise in uncertain times to think about practice and though any such map may not be accurate or complete, it does allow you to consider and think about actions and training required to change behaviours or how spaces and tools are used.
Over the last few years we have seen considerable use made of mapping the use of social networking tools using the concept of Visitors and Residen ts. This was developed by Dave White, Donna Lanclos and Lawrie Phipps into an exercise that could be used to think about a current snapshot of their practice.
ts. This was developed by Dave White, Donna Lanclos and Lawrie Phipps into an exercise that could be used to think about a current snapshot of their practice.
The mapping exercise makes you consider how you are using various tools and what needs to happen to change that map, how do you become more resident when using a tool such as Twitter for example. Or how do you start using a tool which is currently not on your map, such as a professional blog?
The key thing I like to remind people about when using the mapping that this is a continuum and not a distinction between two groups. Your personal Visitors and Residents map is not, and should not be a static thing. The mapping changes as new tools are introduced, old ones retire and your role and behaviours change. The Visitor and Resident mapping exercise in the main covers digital communication, collaboration and participation.
This session discovers if we could we use a similar concept to map teaching practice, curriculum design and learner practices? Sometimes it’s not just about knowing where you are, and where you need to be, but how you get there”.
References
Clay, James (2016) Mapping the learning and teaching
http://elearningstuff.net/2016/01/14/mapping-the-learning-and-teaching/
Visitors and Residents: A new typology for online engagement by David S. White and Alison Le Cornu. First Monday, Volume 16, Number 9 – 5 September 2011 http://firstmonday.org/ojs/index.php/fm/article/view/3171/3049
White, David (2016) Visitors & Residents – navigate the mapping
http://daveowhite.com/vandrworkshops/
Lanclos, Donna (2016) Ta Dah! The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Doing a Visitors and Residents Workshop
http://www.donnalanclos.com/?p=570
Phipps, Lawrie (2016) Mapping for Change
http://lawriephipps.co.uk/?p=8305
Designing quick and effective games for learning
Workshop on game based learning in HE
Wednesday 26 April 14:15-16:15
Led by Alex Moseley, National Teaching Fellow, University of Leicester
This workshop is open to LSE academics, students and external participants: Book a place
 Simulations and complex digital games need time, money and design/technical expertise to develop. Many educators have great ideas for games yet lack the resources to put them into practice (either technically or in game design terms).
Simulations and complex digital games need time, money and design/technical expertise to develop. Many educators have great ideas for games yet lack the resources to put them into practice (either technically or in game design terms).
Alex Moseley and Nicola Whitton have therefore created a fast, fun, ten-step workshop for educators, built around the same design process that games designers use, to allow small teams to quickly develop games for learning: either as fully-fledged traditional games, or as prototypes for simple digital games.
Workshop participants will leave with a skill set for identifying, applying and designing games for learning; and with ideas to apply to their own subject areas.
—————————————————————————————————————————
Ahead of the workshop we interviewed Alex to find out more information about his experience with games
1.How/why did you first become interested/involved in games based learning?
It all started when a card dropped out of my Sunday newspaper. On it was a slightly cryptic, but interesting puzzle – that led me into the centre of an alternate reality game (ARG) called Perplex City. A few months later, I found myself fully immersed (spending hours researching naval signalling flags, and other odd behaviour) and also noticed that many others were as immersed in the game as me, many even more so. Comparing this to the interest shown by my students in my History 101 class, I decided it was worth finding out what engaged the Perplex City players so completely in learning-related tasks. I interviewed the 50 most engaged players, and from that developed a set of key features that I thought could work in education to increase engagement with learning.
2. What type of games have you used in your own teaching?
My first games-based teaching flowed directly from this. I applied the key features from ARGs to my History module, developing an online problem solving game that kept students fed with a constant supply of new challenges, was wrapped in a ‘mystery’ narrative, and saw students battling with each other on a public leader board to win one of a number of prizes. Eight years on, the game still runs each year, and sees students work far more than they need to, pass with an average 2:1 mark, and develop key skills and make key friendship groups to last them for their whole programme.
I have since developed versions of the game for Archaeology and English, and also regularly run workshops with Museum Studies Masters students who develop games for museum education contexts. My latest work is in medical education: working with the Wellcome Collection and healthcare departments internationally to develop simple card games to help medical students to apply knowledge and develop narrative skills in a fun, creative way.
In staff training contexts, I have developed a board game to help programme teams test curriculum designs, and for many years now have been developing play- and game-based approaches to engage conference attendees with the themes or aims of events (running increasingly more encompassing activities for up to 600 participants at ALT-C, Museums and the Web, FOTE, etc.).
3. Gamification and game based learning seems to becoming more popular in higher education, why do you think this is? What do games do that is different to traditional teaching formats?
Games appear to offer a solution to two of the most recurring themes in higher education: student engagement and teaching innovation. Sadly, this often leads to an assumption that any game-like activity will be both engaging and innovative – whereas of course games are just like an academic course: if they’ve been designed well for that context, there’s a chance that students will engage with them. In recent years, it’s been great to see an increase in simple, traditional or low-fi web games for learning; or playful activities that promote creativity and exploration. It’s much easier for a lecturer to see someone use Playdoh in their teaching and think “I could do that!”; or play a card game and then have a go at creating their own.
4. What advice would you give to teachers thinking about introducing games into their teaching?
Think small, cheap, and fun. The most difficult part is deciding what you’d like your game or playful activity to cover: is it a key concept, or a set of ‘knowledge’? Then draw on your own experience of games/sports etc. to see if there are elements that work particularly well with this chosen theme: simple examples might be to use a dice roll to represent randomness in genetics; or top trumps to compare characteristics of chemical compounds, or representing creative writing through a piece of folded paper (write one line, and the starting word on the next, then fold and pass on to the next student)…
Then try it. It probably won’t work too well the first time, but you’ll get ideas of how to improve it (often from the students themselves). Add depth or complexity as needed over time, but keep that core simplicity at its heart.
————————————————————————————————————————-
Those interested in gaming may also be interested to know about two other events
17-18 November Playful learning Special Interest Group meeting – This group is Chaired by Alex and hosts meetings around the country with the upcoming event being hosted in London. It’s free to attend, whether a member of the group or not, simply apply on the event page.
30 November Copyright Community of Practice – The monthly meeting for November will be a chance to play several copyright games. The Copyright Community of Practice group is an informal forum for LSE staff interested in discussing copyright matters for more information go to the Staff training and development system.
Copyright, reading lists and Moodle
 Just before the start of term there was some exciting news in the world of copyright, when the Copyright Licensing Agency (CLA)’s new higher education licence was launched. Also importantly the limit of 5% of a work has been increased to 10% – hurray I hear you say! In case you didn’t know, the CLA licence is what covers you to make photocopies for students for use in teaching, it’s a blanket licence, but there are some important limits and exclusions. The licence also covers scanning, and for many years we have offered a highly efficient Epack service (now called Scanned Readings service) in the library. So why do we do this?
Just before the start of term there was some exciting news in the world of copyright, when the Copyright Licensing Agency (CLA)’s new higher education licence was launched. Also importantly the limit of 5% of a work has been increased to 10% – hurray I hear you say! In case you didn’t know, the CLA licence is what covers you to make photocopies for students for use in teaching, it’s a blanket licence, but there are some important limits and exclusions. The licence also covers scanning, and for many years we have offered a highly efficient Epack service (now called Scanned Readings service) in the library. So why do we do this?
Well partly, because scanning readings under the CLA Licence has certain terms and conditions that must be followed such as the requirement to report every scan we deliver to students annually to the CLA. You also need to check if material is covered by the licence, and make sure you don’t copy more than one chapter from a book, one journal article from an issue or 10% of the work – which ever is greater applies. So it’s really important that staff use the Scanned Readings service so we can stay compliant with our CLA Licence. Did you know we pay a little over £7 per full time student for the licence each year, but that money is in fact returned to the authors and publishers of the work? If you write books and articles you should make sure you have registered with the Authors Licensing and Collecting Society (ALCS) as you’ll see some of that money (which compensates you for possible loss of sales) returned to you.
In addition, the Library have started using a new service delivered by the CLA with the British Library, so host the readings on a Digital Content Store, so you simply need to add links to the files from Moodle. It simplifies things but also helps ensure we can get access to readings that might have been scanned at other universities, and ultimately it will improve the quality of the readings. Please don’t think it saves time and effort by scanning readings or using PDFs you download from e-journals in Moodle. It’s breaking copyright laws but also ultimately not demonstrating to students how to use content ethically, that rewards and gives credit to the original author. And using the Reading List system is also the best way to help direct students to the resources we already pay for. If you would like to find out more about how it works with Moodle, then do get in touch with your Academic Support Librarian.
 If you are baffled by copyright and would like to find out more, then please do consider coming along to a copyright workshop we run each term, where through playing Copyright the Card Game, you can develop and test out your copyright knowledge. The next session is on Monday 14th November. Additionally if you have any queries you are also welcome to attend the Copyright Community of Practice, which runs every month, and is an informal forum for those interested in discussing copyright matters. Or you can drop a line to LTI’s Copyright and Digital Literacy Advisor, Dr Jane Secker (email j.secker@lse.ac.uk), who will be more than happy to test her own knowledge to help you figure out your copyright conundrum. So don’t just copy, copy it right, and don’t be scared of copyright, after all it offers you as an author a lot of protection, and by learning more about the law you can understand what is possible for teaching and research.
If you are baffled by copyright and would like to find out more, then please do consider coming along to a copyright workshop we run each term, where through playing Copyright the Card Game, you can develop and test out your copyright knowledge. The next session is on Monday 14th November. Additionally if you have any queries you are also welcome to attend the Copyright Community of Practice, which runs every month, and is an informal forum for those interested in discussing copyright matters. Or you can drop a line to LTI’s Copyright and Digital Literacy Advisor, Dr Jane Secker (email j.secker@lse.ac.uk), who will be more than happy to test her own knowledge to help you figure out your copyright conundrum. So don’t just copy, copy it right, and don’t be scared of copyright, after all it offers you as an author a lot of protection, and by learning more about the law you can understand what is possible for teaching and research.
Research in the age of Wikipedia
Copyright and Digital literacy advisor Jane Secker reports live from Prague on her recent work on information and digital literacy.
I’m really excited to be pre senting at the European Conference on Information Literacy which this year is being held in Prague from 10th -14th October. This is the fourth conference and I’ve been lucky enough to attend every year since the conference started in 2013 in Istanbul. I went to Dubrovnik in 2014, Tallinn in 2015 and this year I am in Prague. The focus of the conference is information literacy, and many papers address issues related to digital literacy as well. It’s a European conference but in fact people come from all over the world, so it’s a fantastic place to get a global perspective on the work I do at LSE to support staff and students develop their digital literacy. The conference also has a strong link with the work I do to provide support and education in copyright matters. This year there are nearly 300 delegates from over 50 countries with just 19 from the UK. The conference theme is about information literacy in the inclusive society and we’ve had keynotes from Tara Brabazon and Jan Van Dijk.
senting at the European Conference on Information Literacy which this year is being held in Prague from 10th -14th October. This is the fourth conference and I’ve been lucky enough to attend every year since the conference started in 2013 in Istanbul. I went to Dubrovnik in 2014, Tallinn in 2015 and this year I am in Prague. The focus of the conference is information literacy, and many papers address issues related to digital literacy as well. It’s a European conference but in fact people come from all over the world, so it’s a fantastic place to get a global perspective on the work I do at LSE to support staff and students develop their digital literacy. The conference also has a strong link with the work I do to provide support and education in copyright matters. This year there are nearly 300 delegates from over 50 countries with just 19 from the UK. The conference theme is about information literacy in the inclusive society and we’ve had keynotes from Tara Brabazon and Jan Van Dijk.
I am presenting twice at the conference, firstly in a panel session that was held on Monday, based on outreach and advocacy work I do as Chair of the CILIP Information Literacy Group (ILG). My co-presenters were Sharon Wagg from the Tinder Foundation, who are a charity who work to promote digital inclusion, and Stephane Goldstein, who as well as being a freelance consultant, is the Advocacy and Outreach Officer for the ILG. In our panel we discussed some recent collaborations between librarians in academic sector with those in public libraries, to share their experiences of helping to develop digital literacies and promote digital inclusion. The TeachMeet events ILG and Tinder Foundation organised earlier in the year were a great way that academic and public librarians could share ideas and experience. I was delighted that two colleagues from LSE Library, Andra Fry and Sonia Gomes, attended one of these events in February to share our experiences from the Student Ambassadors for Digital Literacy (SADL) programme we were running for three years, to support LSE undergraduates. The panel discussion encouraged participants to share any digital inclusion initiatives they were involved in around the world. We also discussed what made these collaborations successful and why there might be problems and challenges working in this space. Sharon highlighted the Tinder Foundation’s work with libraries through their digital inclusion fund and it was inspiring to hear about work to support the most vulnerable in society, such as the elderly, job seekers and refugees develop basic and more advanced digital skills.
ECIL is also the spiritual home of copyright literacy, as this was where I first heard about the work of Tania Todorova and her colleagues to survey librarians on a country basis about their knowledge of copyright and requirements for education in this field. This was back in 2014 in Dubrovnik and last year Chris Morrison from the University of Kent and I presented the UK survey results in Tallinn. This year I’m returning to present our latest research, exploring the experiences of UK librarians of copyright, using a research method used in education and information literacy called phenomenography. It’s still early days – we carried out 3 focus groups in higher education and have been juggling work and some pretty intensive data analysis. As neither of us had used phenomenography before we are grateful to the help and advice we received from Emma Coonan and Lauren Smith, as well as several very useful articles they pointed us to. I’m sharing our slides from the ECIL presentation which I delivered on Tuesday morning. It has also been great to catch up with Tania, Serap, Joumana and several of the people who undertook the copyright literacy survey in their own country. Part of what motivated Chris and I to do this research was to understand the fear and anxiety that copyright can create, to look at why it’s a topic many in higher education shy away from learning more about, and use this data to better inform how we develop copyright education. I was struck once again by how important it is to get an international perspective on the work we do, and to see in many cases there are so many things we can learn from others experiences and so much that unites us in our work.
The research and collaboration with Chris has informed my thinking about the best way to provide support for others with copyright queries at LSE. For example, I now use a Copyright Card Game in my workshops, which are a fun and engaging way to learn about copyright. However, being seen as ‘the copyright expert’ can be quite a lonely place, and for me it is important that everyone learns a bit about copyright. This is partly what has motivated me to set up a Copyright Community of Practice at LSE (admittedly I did borrow this idea from Chris who set one up at Kent over the summer). The next session is going to be on the 4th November and it is open to any member of staff at LSE! Meanwhile I will enjoy a few more days in beautiful Prague and return to LSE full of more ideas and possibilities to enhance the support that we provide!
Are you interested in developing students digital and information literacies on your courses? Jane is co-running a workshop with TLC and the library on Thursday 20 October 14:00-15:30
Using good practice and examples from the LSE and elsewhere, this session will focus on how to integrate digital and information literacies into the courses and programmes that you teach.
Book a place via the training and develop system:
https://apps.lse.ac.uk/training-system/userBooking/course/7591852
See our website for more information and guides on digital and information literacy
Michaelmas Term Training Opportunities
Now that term has started and you have (hopefully) settled down, why not take this opportunity to refresh or develop new skills?
Michaelmas Term workshops
Check out our programme of workshops around digital literacy and teaching with technology
On Demand and bespoke
Workshops listed below will run on an on-demand basis when at least three people have expressed their interest via LSE’s training system.
We also offer bespoke training to groups of academics and departments to meet specific requirements. Just choose which one(s) you are interested in from both scheduled and on-demand and contact s.ney@lse.ac.uk to arrange for sessions.
And much more!
Stay tuned for more information on our upcoming exciting event on gamification and playful learning in November!
Crowdsourcing for Massive Engagement
London School of Economics and Political Science embarked on a crowdsourced, gamified approach to education and citizenship, harnessing the massive open online space to engage a community of learners in writing a model UK constitution.
The project is a Campus Technology Innovators Award winner for 2016.
Please visit the Campus Technology website to read more about this innovative project which was led by LSE Professor Connor Gearty of the Institute of Public Affairs (IPA) in partnership with Learning Technology and Innovation
More information on the project can be found on our blog
How at home are you online?
How do you use digital tools? Are you constantly online and using social media or management tools to record your every action, or do you just dip in and out of online resources using them as and when you need?
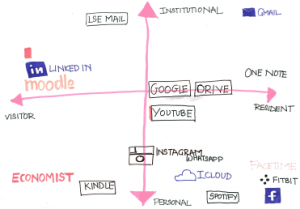
LSE students who have recently taken part in the Students Ambassadors for Digital Literacy project were asked to map their digital footprint to find out more about how they fitted on the Digital Visitors and Residents model (V&R).
The students found significant difference in their use of institutional tools, such as Moodle, LSEforYou, LSE email and their library accounts and personal tools such as Google, Skype and Dropbox.
The exercise encouraged students to think about the overlap with these tools and perhaps how they could utilise them more effectively.
“Drawing a pair of axis, one ranging from Visitor to Resident and the other outlining the nature- Personal or Institutional, we populated the graph with various tools- social media, organisational, entertainment and fitness- from all realms of our being and analysing where we stand for each of them. This method of analysis offers a refreshing way of looking at digital engagement- capturing both the extent and the nature. It allows for subjective interpretation of each tool and hence is not limited by strict definitions. For example, I could put in Microsoft OneNote which I exclusively use for work related documentation.”
However, it may still be too simplistic since it does not account for overlaps well and does not factor in the nature of some tools that are only meant for visitor purposes- eg Moodle. No tool could be on two extremes of a dimension without sketching it in twice- making the chart less succinct. Furthermore, there are other characteristics of engagement that could be factored in with more dimensions: regulated use, open source, within the personal space (entertainment or personal development). These are things we take as banalities and its not until we stop, think and categorise that we can alter and optimise our use of these tools and this would be the biggest takeaway for me from the task”
Simran Masand
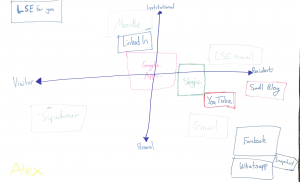
“This process was stimulating as it was good to take a step back from our normal online activities and to understand the extent to which we personally interact with these services. By creating the map, it was significant for me as I noted how we do not always need to act either as a “Visitor” or “Resident”, but rather, this model should be viewed as a continuum. For instance, in my map, I noted how Facebook, even as used as a residential tool, both was within the personal and institutional category due to the fact that I have joined LSE specific groups whilst also having a personal interaction with it.
One point that I came away with from this task was the questioning the extent to which it is possible to be off the scale on the map (i.e. is it possible to be anonymous). However, thinking about this, even for users who may not login to services at all, they will still be classed as a “Visitor” on this model. Therefore, perhaps it is not possible to be completely anonymous whilst we are using online services.”
Alex D’Arcy
Most of the maps showed that students were more likely to act in a visitor mode when accessing institutional tools and behave as residents when using tools to manage their personal lives. This indicates something about how students are engaging and learning at the LSE but also how these tools are presented to them by the School. There is a wider debate about the place of personal tools such as social media in teaching, but perhaps some of the institutional tools are not being used to their full potential. For example Simran mentions in her post that Moodle is “only meant for visitor purposes” yet in fact Moodle is designed using social constructionist pedagogy with the idea that learning is a collaborative cultural event which would encourage ‘resident’ use. Moodle supports the use of discussion forums, peer assessment and feedback, collaborative writing, group submissions, anonymous Q&A, Wiki’s, blogs, and many more activities. If designed well a Moodle course can encourage an online community which supports and extends beyond face to face work carried out in the classroom.
The maps raise several questions about how we separate out our behaviours and identities online. LSE students appeared to leaving a large digital footprint with their use of external applications in their personal life but did not seem as comfortable in creating a professional persona on apps like Linked In or Twitter. One of the aims of the SADL project is to work with students in order to discuss strategies to build a positive online presence and expand their networks. Workshops involve sharing and testing online tools to see how they can be adapted from personal use to manage their academic work.
The student blogs about the workshop and more information about the SADL project can be found on the SADL blog.
Constitution UK wins Campus Technology Teaching and Learning Innovation award
LSE has been awarded with the Campus Technology Teaching and Innovation (pg30) 2016 award for their innovative work on the Constitution UK project which ran in early 2015. The Campus Technology article on the award was published on 17 August 2016.
Constitution UK was a collaborative project that aimed to crowdsource and hack the UK constitution. The project, led by LSE Professor Connor Gearty of the Institute of Public Affairs (IPA) in partnership with Learning Technology and Innovation (LTI), invited individuals to share views and ideas on what should be part of a UK constitution in the 800th anniversary year of Magna Carta. The project generated over 1 million words, thousands of ideas and tens of thousands of votes and resulted in the writing of an 800 word crowdsourced constitution of the UK. Over 1500 community members took part in this large scale public policy and learning project, with over 20 LSE students acting as moderators.
The project utilized innovative methods of engagement, used techniques such as ideation, crowdsourcing, informal learning and gamification conducted through an online platform (Crowdicity) in order to generate engagement that increased over the duration of the course. We engaged social media organisations and special interest groups to ensure successful integration of learning outcomes and the effective and representative engagement of the community in the platform. If you want to know more about the project you check it out here.
This prestigious Teaching and Learning Innovator award by Campus Technology magazine (an industry, leading magazine for online and blended learning professionals) recognises the project in that it ‘…delivered both a public policy success as well as a significant and innovative approach to online learning and engagement.’
“… The awards represent excellence in experimentation, design, collaboration and implementation, and the projects they recognize expand the possibilities for individual campuses and the field of higher education technology,” said Dr. John Hess, program chair, Campus Technology Conference.
“We are extremely proud to have been nominated and then selected for this prestigious award. It recognises an incredibly innovative project that delivered far beyond our wildest dreams. It also recognises the hard work and commitment of many academic and professional staff at the LSE” said Peter Bryant, Head of Learning Technology and Innovation. “It remains the most remarkable project I have ever worked on.” noted Paul Sullivan, the Manager of the IPA.
Creating a Smart Writing Environment with Academic Markdown
In January, Tobias Pester, postgraduate students in the department of International History at the LSE, was awarded an LTI Grant for his project to “develop, document, and teach a Workshop for Sustainable Authorship for students of the LSE that familiarizes and equips them with the writing environment of Academic Markdown”. The workshop will take place on Tuesday, 7th June and a recording will be made available afterwards. Read about his experience of this handy tool.
 In the spring of 2015 I finished my first year of American grad school. Coming from the German university system I knew it was going to be a Protestant re-education camp in terms of work load and ethic. By the end of that spring I had to write three sizeable papers in short succession and ‘time is of the essence’ took on a new meaning. Lucky for me some of my friends had just started using this writing set-up that streamlines all the things that take no brain but lots of time: citations, the bibliography, and worrying about the different format of citations when in footnotes vs. when in the bibliography.
In the spring of 2015 I finished my first year of American grad school. Coming from the German university system I knew it was going to be a Protestant re-education camp in terms of work load and ethic. By the end of that spring I had to write three sizeable papers in short succession and ‘time is of the essence’ took on a new meaning. Lucky for me some of my friends had just started using this writing set-up that streamlines all the things that take no brain but lots of time: citations, the bibliography, and worrying about the different format of citations when in footnotes vs. when in the bibliography.
Enter Academic Markdown and Pandoc. So-called markup languages like LaTeX have long been used by authors in the sciences. They’re great to handle formulas, diagrams and other sciences-specific requirements. For humanist writers, however, the upside to learning a markup language had been comparatively small. All we really need are basic formatting options, block quotes, and citations.
That’s where Markdown comes in handy. It’s designed to satisfy those requirements and be easy to pick up at the same time. It only takes five minutes to learn how to mark a header or a footnote as such and the text remains visually intact and perfectly readable in its raw form. And because formatting, citation management, and bibliography are almost entirely automated it affords an utterly distraction-free work flow. I work on crafting my text and crafting my text only. The last line in my manuscript is the header ‘Bibliography’. When I’m done pouring my blood, sweat, and tears onto the screen, I run it through a simple program called Pandoc once and, voilà, I get a ready-made ´pdf´ or ´docx´ with citations and bibliography according to whichever citation style language I specified.

The text in Academic Markdown and after formatting
Using that particular set-up last spring I became a writing machine. And the many hours freed from formatting could go into refining my argument or polishing my prose. I am since doing all my writing this way, from response papers to my dissertation, from personal letters to invoices. American grad school, however, still kicked my ass.
To share the benefits of this work flow I am developing and teaching a class with the generous help of an LSE Learning Technology and Innovation Grant. The workshop will take place on Tuesday, 7th June, 2-5 p.m. in 32L.LG.18 alongside the Teaching and Learning Centre’s Dissertation Week. Spread the word and join us!
Hit me up on Twitter at @philomonk. I’d love to hear your thoughts! #SmartWriting16